超声波测距
本节课来学习使用 MicroPython 控制超声波传感器并获取距离数据,最终搭配一个蜂鸣器实现倒车雷达的效果。
实验原理
超声波是一种频率高于 20000Hz 的声波,超声波的方向性好,反射能力强,易于获得较集中的声能,在水中传播距离比空气中远,可用于测距、测速、清洗、焊接、碎石、杀菌消毒等。
超声波可用于许多不同的领域。超声波设备用于检测物体和测量距离。超声成像或超声检查常用于医学。在产品和结构的无损检测中,超声波用于检测不可见的缺陷。在工业上,超声波用于清洁、混合和加速化学过程。蝙蝠和鼠海豚等动物使用超声波来定位猎物和障碍物。
本实验使用的超声波模块为 HC-SR04 超声波传感器,其原理为利用超声波在遇到障碍物后反射,结合声波在空气中的传播速度,可以得出传播的距离。该模块外观如下图所示:
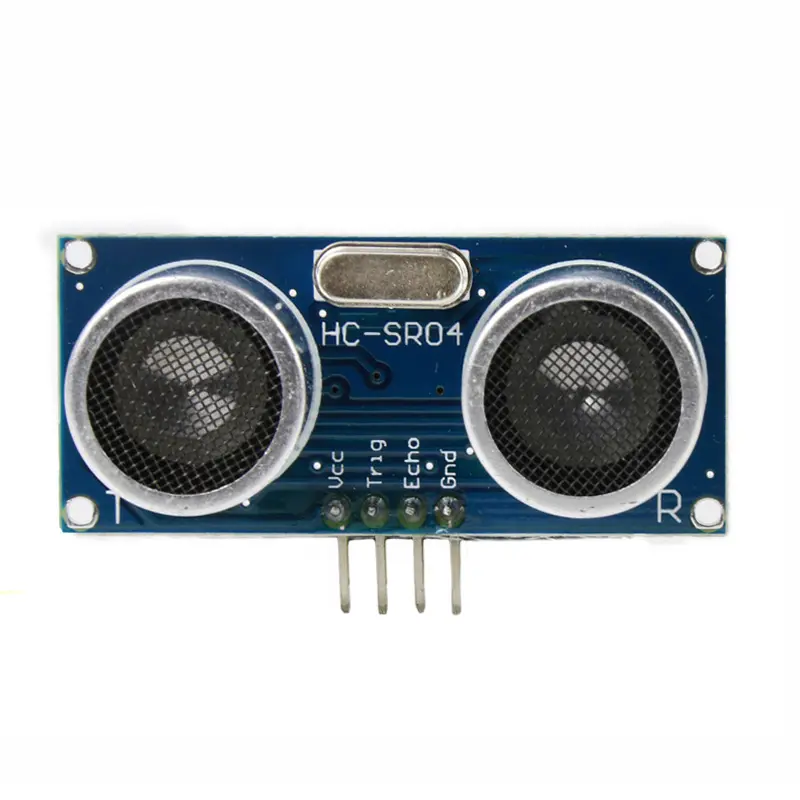

超声波传感器使用声纳来确定与物体的距离。我们使用的超声波模块由 2 个超声波探头组成:
T:表示Transmitter(发射),负责发送超声波信号;R:表示Receiver(接收),负责接收回响信号;
注意
如果在使用过程中,对其中任意一个探头进行遮挡,都会使超声波无法正常测量距离。
底部有四个引脚:
VCC:5V 供电引脚;GND:接地;TRIG:控制信号输入;ECHO:回响信号输出;
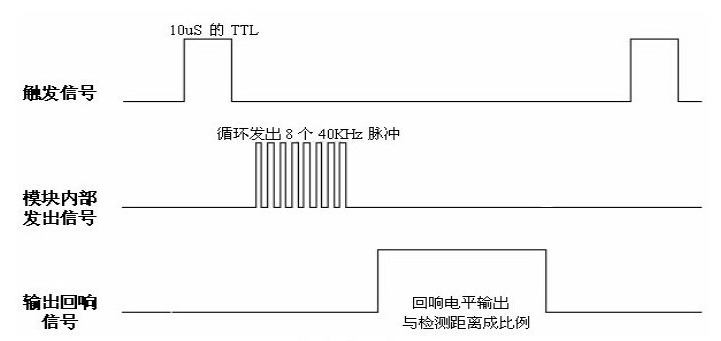
以上时序图表示超声波模块的基本工作原理:
- 采用 IO 口 TRIG 触发测距,给一个 10us 的高电平信号;
- 模块自动发送 8 个 40khz 的方波,自动检测是否有信号返回;
- 有信号返回,通过 IO 口 ECHO 输出一个高电平,高电平持续的时间就是超声波从发射到返回的时间。测试距离=(高电平时间*声速(340M/S))/2
Trig 引脚是用来输入一个长为 10us 的高电平方波,通过输入这一方波,模块会自动发射 8 个 40KHz 的声波,并在这个时刻,Echo 引脚会由 0 变为 1,此时开启定时器定时。当超声波返回并被模块接收到后,Echo 端引脚电平从 1 变为 0,出现下降沿。这时候结束定时,通过计算定时器的值并乘上 340m/s 的声音传播速度,即可计算所测距离。
回响信号的脉冲宽度与所测的距离成正比。由此通过发射信号到收到的回响信号时间间隔可以计算得到距离。公式如下:
距离 = 高电平时间 * 声速(340m/s)/2
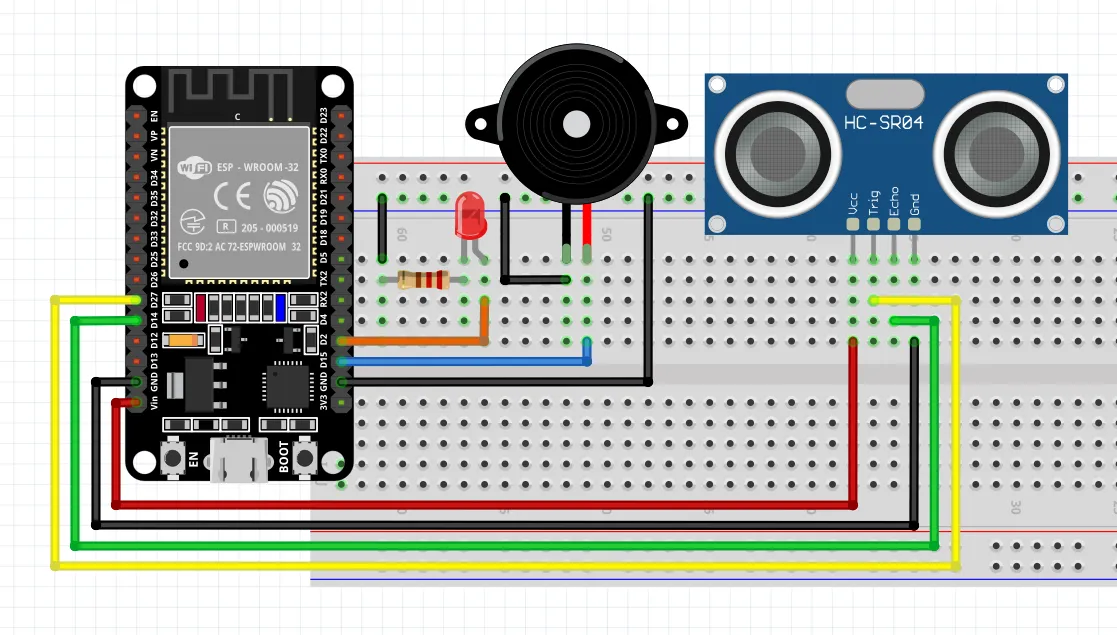
硬件电路设计
物料清单(BOM 表):
| 材料名称 | 数量 |
|---|---|
| 有源蜂鸣器 | 1 |
| LED | 1 |
| 1KΩ 电阻 | 1 |
| 超声波模块 HC-SR04 | 1 |
| 杜邦线(跳线) | 若干 |
| 面包板 | 1 |
软件程序设计
在使用超声波传感器测距时,我们需要用到 machine 模块中的 time_pulse_us(pin, pulse_level, timeout_us=1000000) 方法,具体可以参考 MicroPython 官方手册:
time_pulse_us() 的作用是在给定引脚上为脉冲计时,并返回脉冲持续时长,单位为 us。为低脉冲计时时,pulse_level 参数应为 0;为高脉冲计时时,该参数应为 1。
若引脚的当前输入值与 pulse_level 不同,该函数首先需等待,直至引脚输入与 pulse_level 相等;然后为引脚与 pulse_level 相等的时段计时。若引脚已与 pulse_level 相等,则计时立即开始。
1. 超声波测距
该程序的功能是通过超声波模块测算距离并打印在命令行中,代码如下:
import time
from machine import Pin, time_pulse_us
# 定义echo 与 trig 引脚
echo = Pin(14, Pin.IN)
trig = Pin(27, Pin.OUT)
# 将 trigger 引脚设置为低电平
trig.value(0)
while True:
# 发送一个 10us 的方波脉冲
trig.value(1)
time.sleep_us(10)
trig.value(0)
# 获取脉冲时间
pulse_time = time_pulse_us(echo, 1)
# 根据时间计算距离
distance = pulse_time * 0.3432 / 2
print('距离为: %dmm' % distance)
time.sleep(0.1)
由于 HCSR04 很常用,因此,网上也有很多别人封装好的模块,比如下面代码:
import machine, time
from machine import Pin
__version__ = '0.2.0'
__author__ = 'Roberto Sánchez'
__license__ = "Apache License 2.0. https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0"
class HCSR04:
"""
Driver to use the untrasonic sensor HC-SR04.
The sensor range is between 2cm and 4m.
The timeouts received listening to echo pin are converted to OSError('Out of range')
"""
# echo_timeout_us is based in chip range limit (400cm)
def __init__(self, trigger_pin, echo_pin, echo_timeout_us=500*2*30):
"""
trigger_pin: Output pin to send pulses
echo_pin: Readonly pin to measure the distance. The pin should be protected with 1k resistor
echo_timeout_us: Timeout in microseconds to listen to echo pin.
By default is based in sensor limit range (4m)
"""
self.echo_timeout_us = echo_timeout_us
# Init trigger pin (out)
self.trigger = Pin(trigger_pin, mode=Pin.OUT, pull=None)
self.trigger.value(0)
# Init echo pin (in)
self.echo = Pin(echo_pin, mode=Pin.IN, pull=None)
def _send_pulse_and_wait(self):
"""
Send the pulse to trigger and listen on echo pin.
We use the method `machine.time_pulse_us()` to get the microseconds until the echo is received.
"""
self.trigger.value(0) # Stabilize the sensor
time.sleep_us(5)
self.trigger.value(1)
# Send a 10us pulse.
time.sleep_us(10)
self.trigger.value(0)
try:
pulse_time = machine.time_pulse_us(self.echo, 1, self.echo_timeout_us)
return pulse_time
except OSError as ex:
if ex.args[0] == 110: # 110 = ETIMEDOUT
raise OSError('Out of range')
raise ex
def distance_mm(self):
"""
Get the distance in milimeters without floating point operations.
"""
pulse_time = self._send_pulse_and_wait()
# To calculate the distance we get the pulse_time and divide it by 2
# (the pulse walk the distance twice) and by 29.1 becasue
# the sound speed on air (343.2 m/s), that It's equivalent to
# 0.34320 mm/us that is 1mm each 2.91us
# pulse_time // 2 // 2.91 -> pulse_time // 5.82 -> pulse_time * 100 // 582
mm = pulse_time * 100 // 582
return mm
def distance_cm(self):
"""
Get the distance in centimeters with floating point operations.
It returns a float
"""
pulse_time = self._send_pulse_and_wait()
# To calculate the distance we get the pulse_time and divide it by 2
# (the pulse walk the distance twice) and by 29.1 becasue
# the sound speed on air (343.2 m/s), that It's equivalent to
# 0.034320 cm/us that is 1cm each 29.1us
cms = (pulse_time / 2) / 29.1
return cms
2. 自定义 HCSR04 类
我们可以通过学习他人的代码,并将其转化为自己的代码,从而加深学习,提高自己的编程能力,下面是我仿写的代码:
import time
from machine import Pin, time_pulse_us
# 定义 HCSR04 公共类
class HCSR04:
def __init__(self, trigger_pin, echo_pin):
# 初始化 trigger 与 echo 引脚
self.trigger = Pin(trigger_pin, Pin.OUT)
self.echo = Pin(echo_pin, Pin.IN)
# 将 trigger 引脚设置为低电平
self.trigger.value(0)
def get_distance(self):
# 初始化传感器
self.trigger.value(0)
time.sleep_us(5)
# 通过 T 探头发送 1 个 10us 的脉冲
self.trigger.value(1)
time.sleep_us(10)
self.trigger.value(0)
# 获取脉冲时间
pulse_time = time_pulse_us(self.echo, 1)
# 根据时间计算距离
distance = pulse_time * 0.3432 / 2
return distance
提示
第三方代码尽量放在 libs 目录中,自己写的代码放在 common 目录下
然后,我们就可以调用该模块中的 HCSR04 公共类了,代码如下:
import time
from common.hcsr04 import HCSR04
# 定义 HCSR04 对象
sensor = HCSR04(27, 14)
while True:
# 获取测量距离
distance = sensor.get_distance()
print('距离为: %dmm' %distance)
time.sleep(0.1)
3. 倒车雷达系统
最后,我们可以根据获取的距离来实现倒车雷达的效果,距离近的时候蜂鸣器会报警,LED 闪烁,随着距离越来越近,蜂鸣器发生频率与 LED 的闪烁频率都会越来越频繁,代码如下:
import time
from machine import Pin
from common.hcsr04 import HCSR04
# 定义 HCSR04 对象
sensor = HCSR04(27, 14)
# 定义蜂鸣器与LED对象
buzzer = Pin(15, Pin.OUT)
led = Pin(2, Pin.OUT)
# 初始化
buzzer.value(0)
led.value(0)
while True:
# 获取距离
distance = sensor.get_distance()
print('距离为: %dmm' % distance)
# 如果距离过近则报警,距离越近,报警越频繁
if distance < 200:
delay_time = int(distance)
buzzer.value(1)
led.value(1)
time.sleep_ms(delay_time)
buzzer.value(0)
led.value(0)
time.sleep_ms(delay_time)
else:
buzzer.value(0)
led.value(0)
time.sleep(0.1)
